
Spanish Regulations
Pladur® Systems and products comply with the requisites of Spanish regulations.
Spanish Technical Building Code
The Spanish Technical Building Code (CTE) is the regulatory framework which establishes the requirements to be met by buildings in relation with the basic safety and habitability requirements laid down in the Spanish Building Standards Act no. 38/1999 of 5 November (LOE).
The scope of the Spanish Technical Building Code which affects our Pladur® systems is defined in the following Basic Documents:
- DB SI: Safety in Case of Fire.
- DB HE: Energy conservation.
- DB HR: Protection from noise.
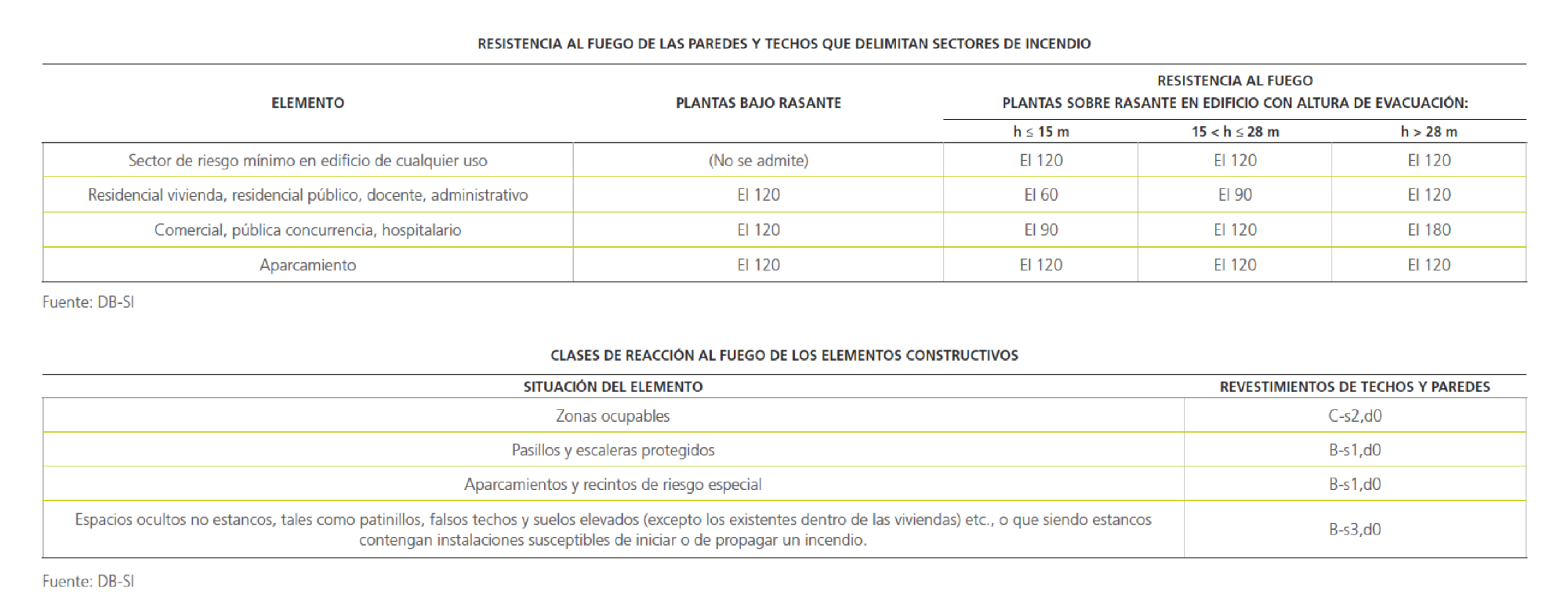
DB SI: Safety in Case of Fire.
The DB-SI (Basic Document on Safety in Case of Fire of the Technical Building Code) specifies the basic requirements relating to safety in case of fire in buildings, along with the procedures for complying with the regulations.
Some CTE requirements are shown in the following tables. However, justification of the projects will necessitate a detailed procedure which meets the CTE requirements. Below we include some basic CTE tables.
DB HE: Energy conservation
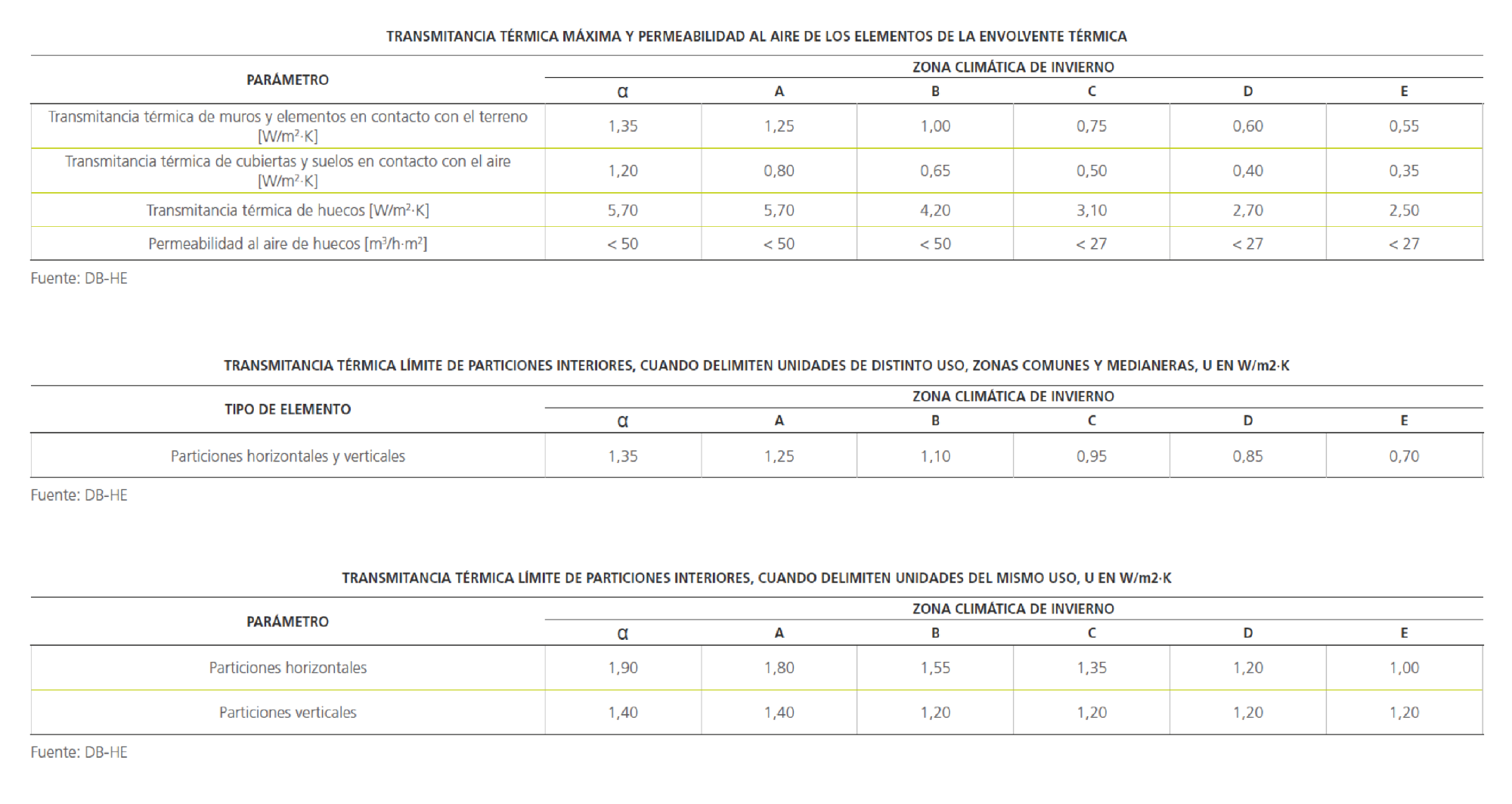
The DB-HE (Basic Document on Energy Conservation) of the Technical Building Code (CTE) in Spain establishes the demands for complying with the energy requirements in buildings. Criteria and procedures are established for assessing thermal insulation, energy demand and consumption, etc.
To select the thermal performance of our Pladur® systems, we follow the requirements laid down by the Spanish Technical Building Code. There is a technical and social intention to guarantee in the coming years mechanisms which will permit achieving buildings with almost zero energy consumption.
The DB-HE proposes a zoning of energy demand according to defined climatic zones. The standard determines the climatic zone and the maximum thermal transmittance of closures and interior partitions.
To follow the regulations contained in the DB-HE, it is advised to study the requirements set out in the tables, as they show the maximum thermal transmittance of interior partitions.
The DB-HE 1 sets out the limits on energy demand applicable to existing or new buildings. The limits on energy demand are established according to the climatic zone, the locality in which the building is situated and its use, and according to characteristics like its orientation, percentage of openings, etc.
DB HR: Protection from noise.
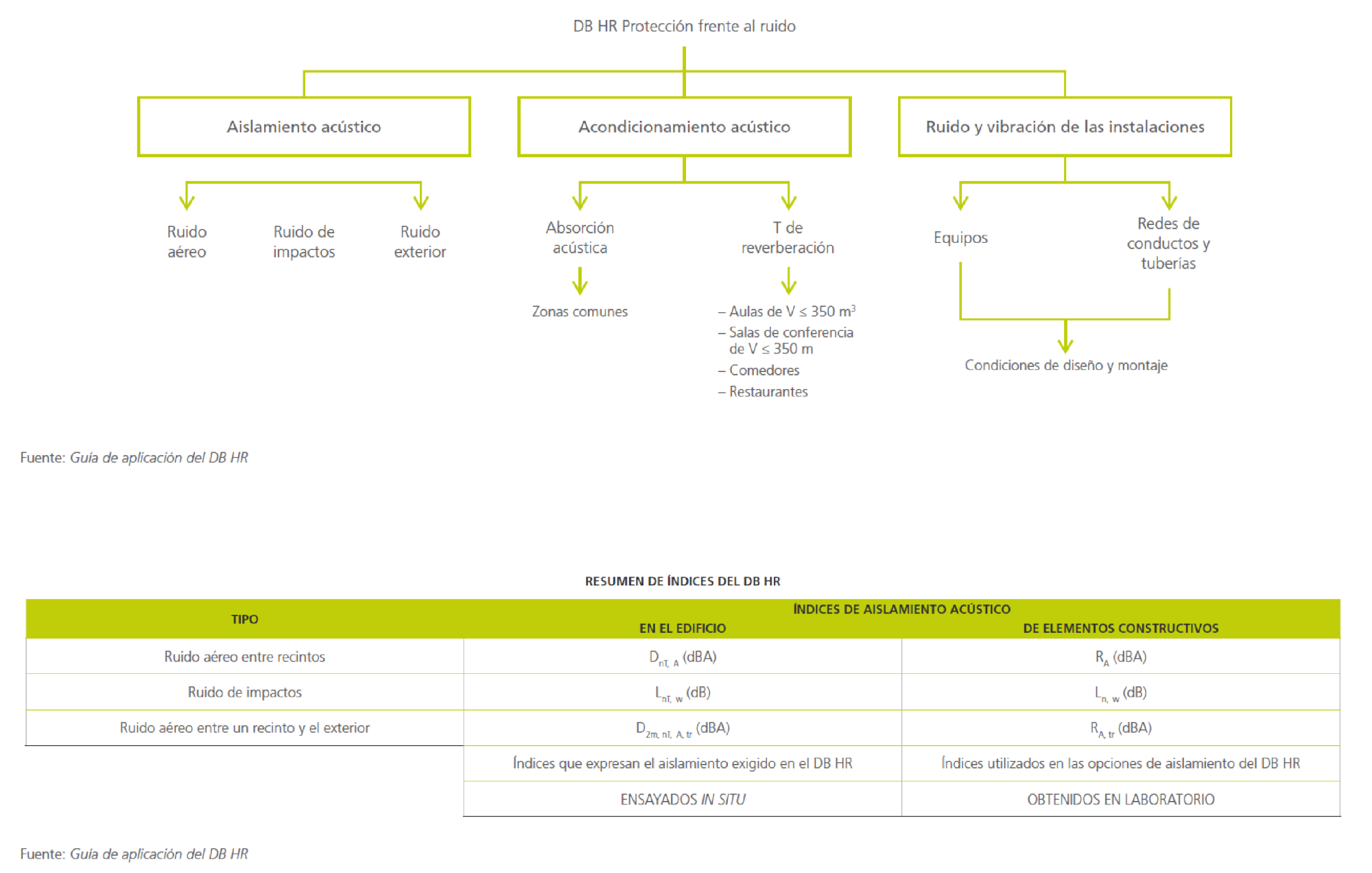
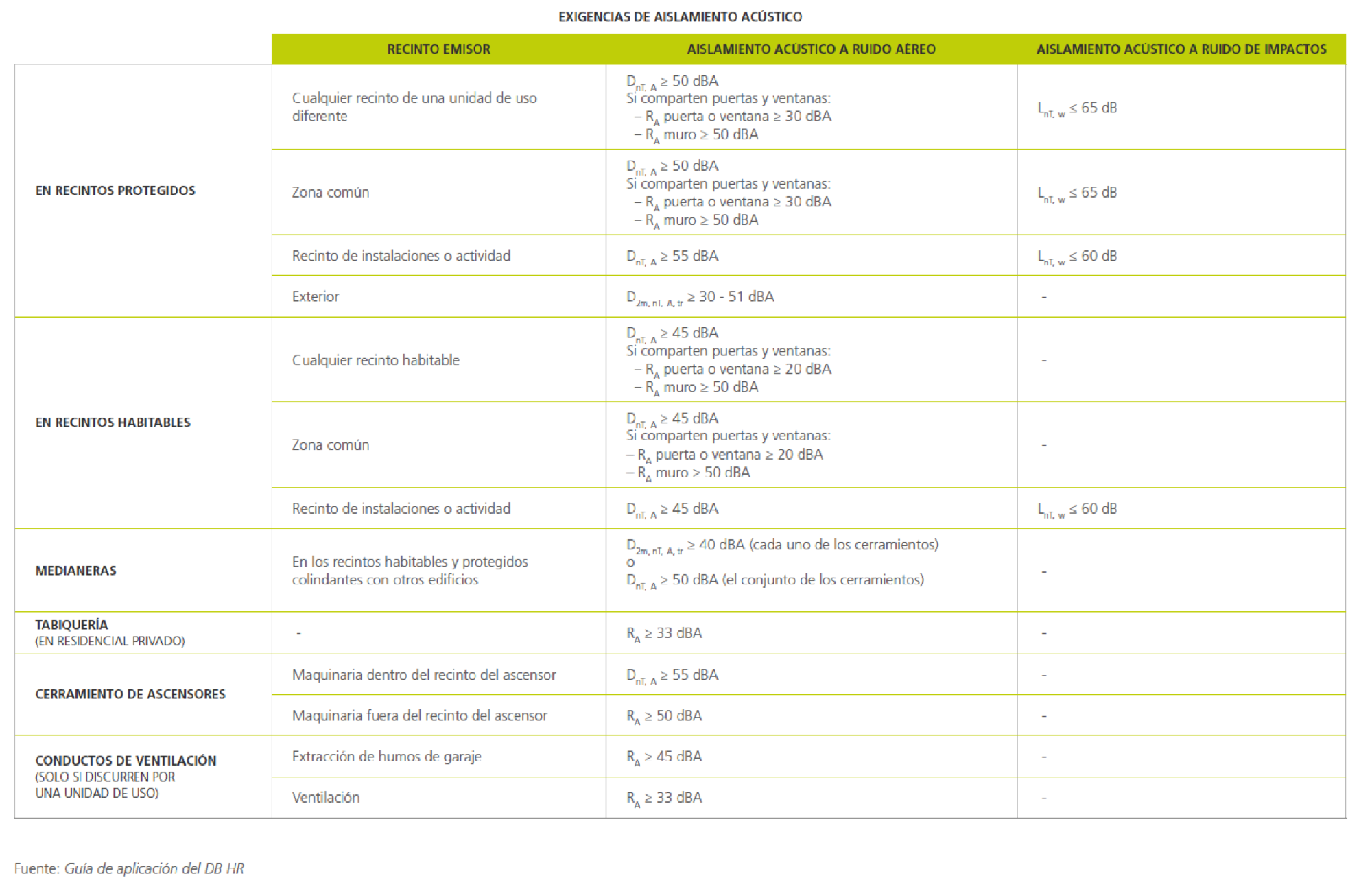
The DB HR (Basic Document on Protection from Noise) of the Spanish Technical Building Code establishes the acoustic conditions of buildings and regulates the following aspects:
- Acoustic insulation is the parameter that indicates the degree of protection from noises generated by the external surroundings or from adjacent enclosures as a result of installations or activities proper to the building.
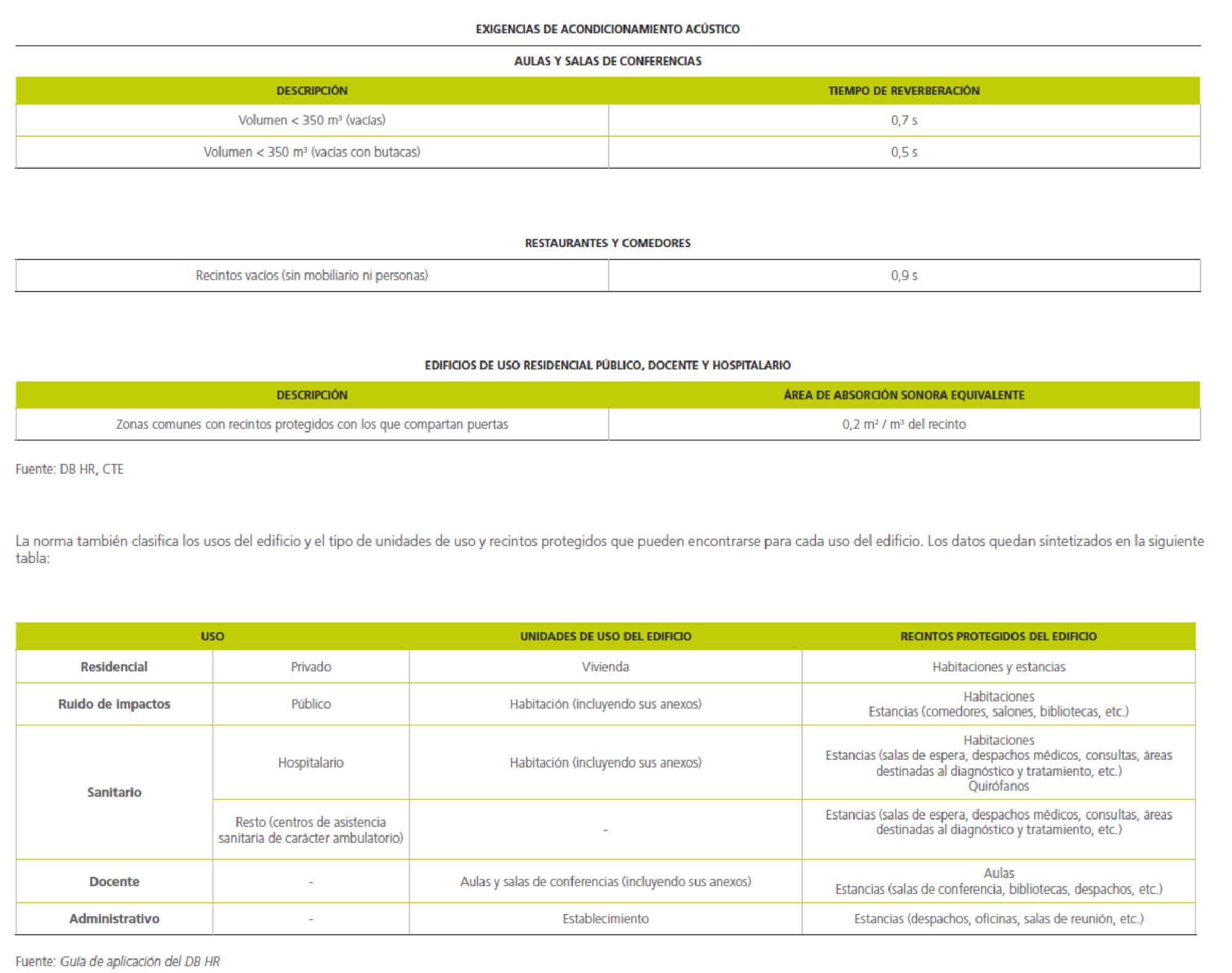
- Acoustic insulation seeks to improve the acoustic comfort inside the enclosures by reducing the reverberation time, using sound-absorbing materials.
- Noise and vibrations from the installations of the devices and piping systems of buildings.
In regard to acoustic insulation, the requirements of the DB HR are applied to buildings with the following uses:
- Public residential building: hotels, residences, etc.
- Private residential building: homes.
- Sanitary facilities: hospitals and outpatient centres.
- Educational centres: schools, universities, music schools, etc.
- Administrative settings: offices.
The scope of application excludes buildings of public use, commercial use, car park buildings, etc.
The following types of enclosures exist:
- Habitable.
- Protected
- Non-habitable.
- Of installations.
- Of noisy activity.
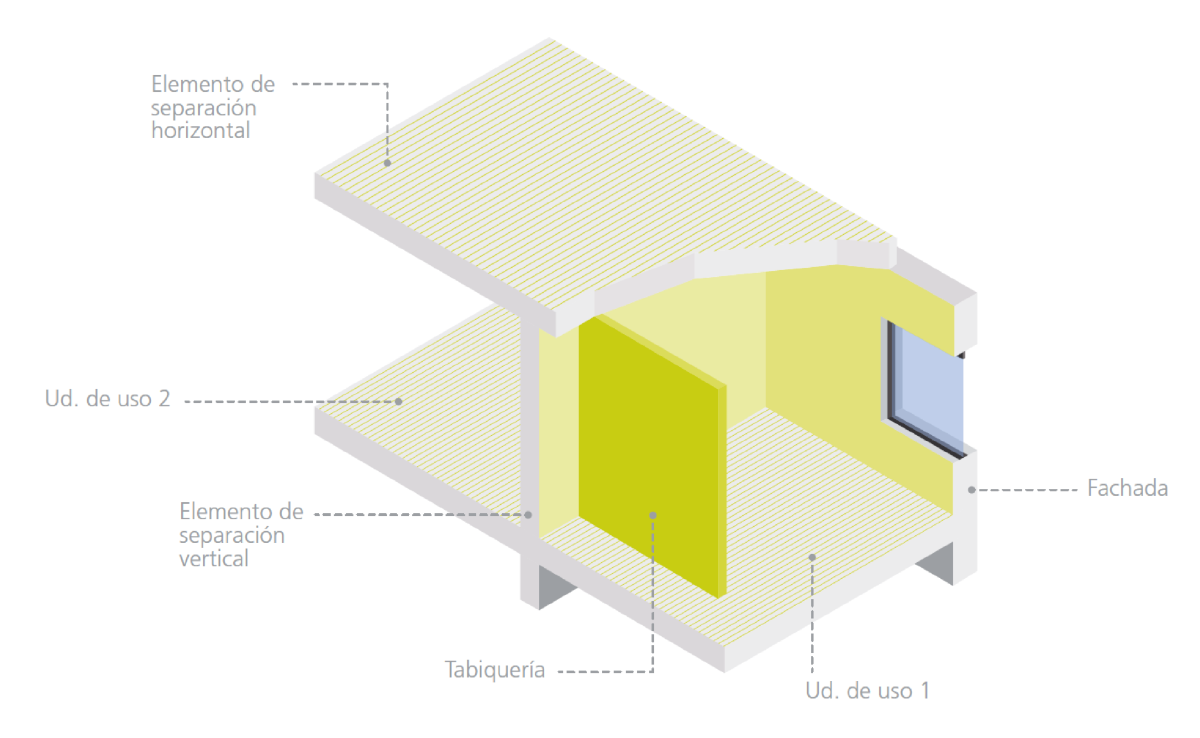
The DB HR defines the following concepts in this context:
- Use unit: Building or part of a building allocated to a specific use and whose users are interlinked, either due to belonging to the same family unit, company or corporation, or due to forming part of a group or collective which performs the same activity. In any case, the following are considered use units:
a) in residential buildings, each one of the homes;
b) in hospital-use buildings and public residences, each room, including its annexes;
c) in teaching centres, each classroom or meeting room, including its annexes.
- Common areas: Zones which provide a service to several use units.
According to the DB HR, there are two procedures for defining the acoustic solutions for the building:
- The simplified option, with constructive solutions laid out in tables.
- The general option of calculation based on the UNE-EN 12354 standard, parts 1, 2 and 3.
The following table summarises the requirements of the Standard:
STANDARD UNE 102043: Installation of construction systems with gypsum plasterboards (PYL)
This is a Spanish standard for producing constructive systems using laminated plasterboard. It defines the various types of products and systems that can be created by means of laminated plasterboard solutions. It also defines the calculation method of systems of partition walls, claddings and ceilings and provides recommendations for their correct execution.
