
Acoustic Conditioning
Designing acoustically comfortable environments is essential to achieve quality rooms.
Acoustic conditioning or correction involves diffusing sound in a room by changing the level of absorption or reflection by walls.
Why fit out an enclosure?
Acoustic comfort,
quality of the premises
Improve communication, understanding and functionality of the venue
Reducing risks
Improve the
productivity
Space functionality
Each space or room will have different acoustic requirements, depending on use. It is important to identify these requirements when designing a space and define the most appropriate solution systems.
Intelligibility
I want to be understood
Confidentiality
I don't want other people to hear me
Concentration
I don't want to be disturbed
In practical terms, acoustic conditioning for a space should be planned to ensure it is the most suitable for future use. By way of example, acoustic conditioning for a library or classroom should be based on technical criteria that will clearly differ from those for a concert hall, given the different functions and requirements. This means specific solutions are adopted for each situation.
Pladur® offers solutions for both acoustic insulation and conditioning. The Pladur® FON+ range of ceilings range includes over 100 different models of continuous and drop ceilings, meeting the highest standards for both acoustic conditioning and design and appearance.
Sound absorption
From an architectural perspective, the key aspects of acoustic conditioning are the geometry of the space and the absorption of the building elements that shape it.
El mecanismo de absorción acústica se basa en la disipación de la energía sonora que incide sobre un material absorbente a través de diversos mecanismos físicos. Las prestaciones absorbentes de los materiales se cuantifican mediante el denominado coeficiente de absorción α, que se define como la relación entre la energía absorbida por el material y la energía incidente sobre el mismo.
This coefficient is understood 0 (completely reflective material) and 1 (complete absorption), the value of α is directly related to the physical properties of the material and varies with frequency.


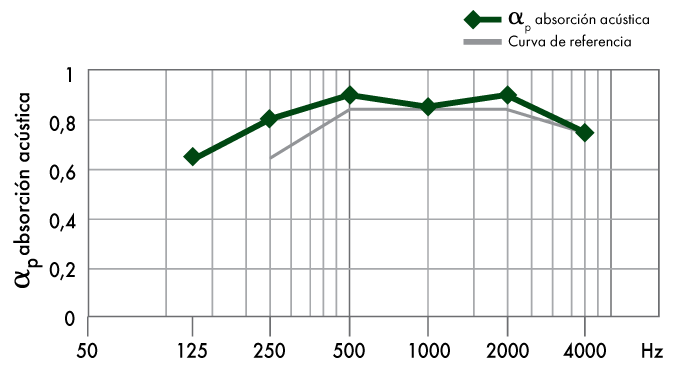
Sound absorption coefficient
The sound absorption coefficient depends on the frequency, as shwon in the chart. In a specific system, there is determined coefficient absorption ap, that matches each frecuency. be seen in the graph. To simplify the the process, various normalized procedures are used to synthesise the frequency information into single value. The most widely used normalized procedures for obtaining this global value are the αw index and the NRC index.
The weighted sound absorption coefficient αw: this coefficient is the standardised index established under the ISO 11654 ragulation to express the sound absorption level of a material based on its frequences. αw will correspond to the 500 Hz value of the largest normalised curve between 250 and 4000 Hz, where adding the differences between the materal´s absorption curve and the benchmark curve is less is less than 0.1.
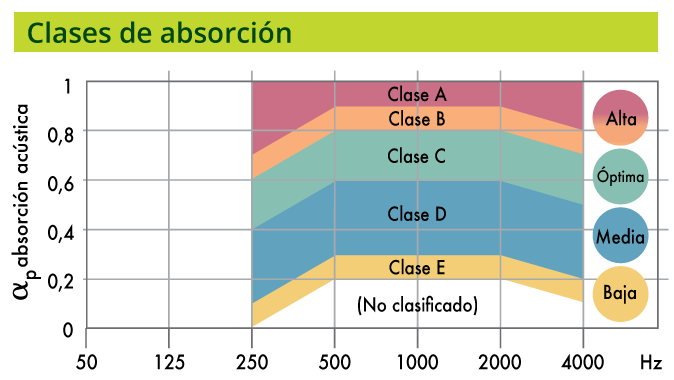
This coefficient may show the indicator as “L=Low”, “M=Medium” or “H=High” if the practical noise reduction coefficients exceed those of the displaced reference curve by 0.25 or more in their different frequency spectra.
Depending on the value of the weighted noise reduction coefficient, the standard provides a classification for absorbent materials ranging from class A (maximum absorption) to class E.
The mean reduction coefficient: αm: this is a scale whose value is obtained by calculating the mean of the practical noise reduction coefficients in the bands of 500, 1000 and 2000.
Noise reduction coefficient (NRC): this is provided by American Standard ASTM C423. It is obtained from the mean noise reduction coefficient for the octave bands of 250, 500, 1000, 2000 and 4000 Hz.
The current Spanish standard (CTE) defines the requirements for DB-HR compliance for the coefficients αw and αm .
Noise reduction is directly related to reverberation time.
Reverberation time (RT) is a parameter that refers to the time interval required to verify a drop in noise level to 60 dB, after the source of the noise emission has stopped.
En función del valor del coeficiente de absorción sonora ponderado, la norma indica una clasificación para los materiales absorbentes que va desde la clase A (máxima absorción) hasta la clase E.
El índice NRC (Noise Reduction Coefficient): es el contemplado en la norma americana ASTM C423. Se obtiene promediando el coeficiente de absorción sonora correspondiente a las bandas de octava de 250, 500, 1000, 2000 y 4000 Hz.
El coeficiente de absorción media αm: es un escalar cuyo valor se obtiene de calcular el promedio de los valores de los coeficientes de absorción sonora práctico en las bandas de 500, 1000 y 2000.
La actual normativa española (C.T.E.) define aportar para el cumplimiento del DB-HR los coeficientes αw y αm .
La absorción acústica mantiene una relación directa con el tiempo de reverberación.
El tiempo de reverberación (Tr) es un parámetro que corresponde al intervalo de tiempo necesario para verificar un descenso del nivel sonoro de 60 dB, después de interrumpir la fuente de emisión sonora.
Providing appropriate acoustic conditioning for a given space necessarily involves taking into account the frequency characteristics of the noise. For instance, we can intuitively identify a bass sound as one with predominantly low frequencies, while high frequencies predominate in a treble sound. Adequate acoustic conditioning will provide comfortable sound ambience characterised by balanced atmospheric noise in terms of frequency distribution.

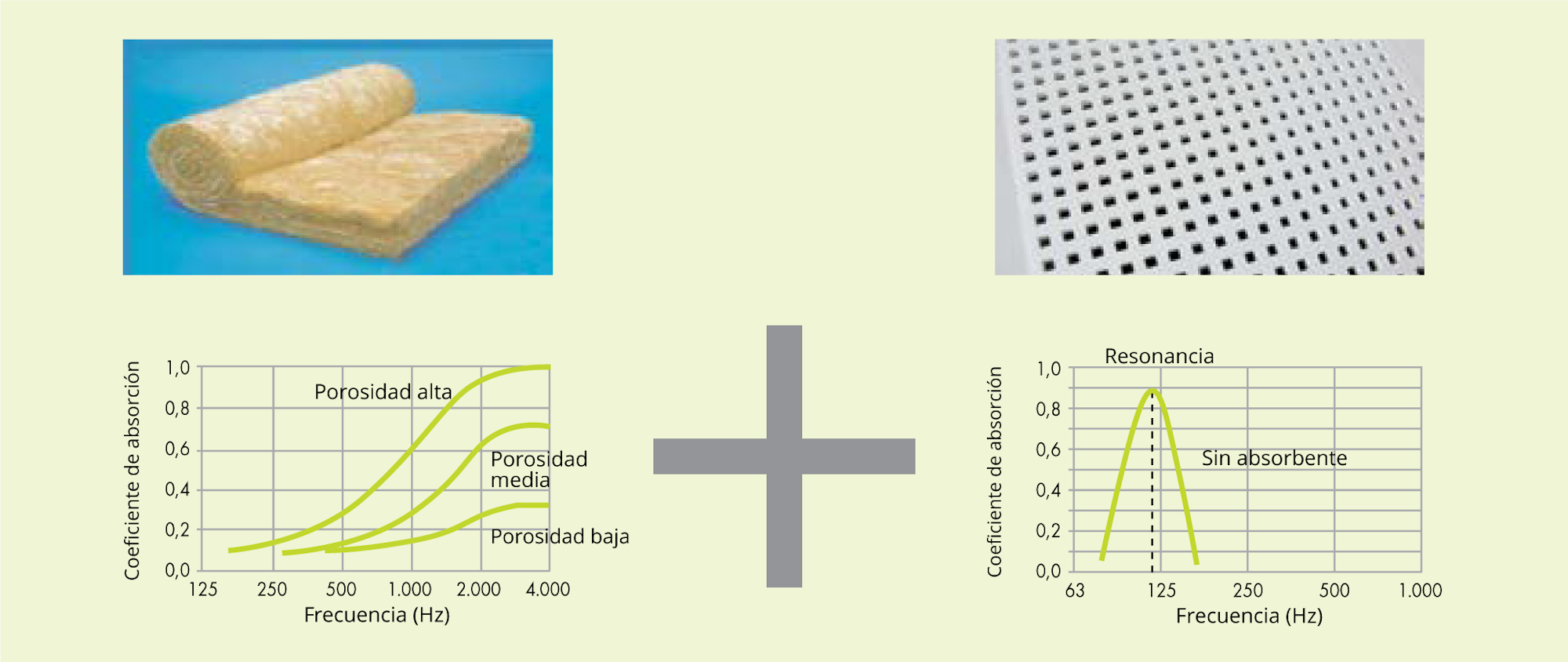
There are numerous construction products and systems to improve acoustic conditioning, each one with different qualities and applications. In general terms, porous and fibrous absorbent materials are good at absorbing high frequencies, while resonator-based systems provide good low frequency absorption at a narrow frequency range. Pladur® FON+ systems combine the characteristics of both types, thus providing excellent sound absorption qualities.
Related Products
Ceiling FON+ C3-8

Ceiling FON+ C3-8
Pladur® FON+ improves acoustic comfort in all premises where it is installed.
Ceiling FON+ Tweed

Ceiling FON+ Tweed
For spaces requiring acoustic conditioning treatment or a distinctive decorative touch.
Ceiling FON+ R8

Ceiling FON+ R8
For spaces requiring acoustic conditioning treatment or a distinctive decorative touch.
Ceiling FON+ Verde

Ceiling FON+ Verde
For spaces requiring acoustic conditioning treatment or a distinctive decorative touch.






